Calculates various distribution or density functions.
Syntax
Distribution(X, Distribution, Parameter1 [ , Parameter2 ])
The syntax of the Distribution function consists of the following parts:
Part |
Description |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
X |
Contains the X values, i. e. the values of the random variable for which the distribution function or density function is to be calculated. When calculating a discrete distribution, the X values must be integral and positive. Permitted data structures are Scalar value, Data series and Data matrix. All numeric data types are permitted. For complex data types the absolute value is formed. If the argument is a list, then the function is executed for each element of the list and the result is also a list. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Distribution |
Specifies which distribution is to be calculated and whether the distribution function or density function is to be calculated. The argument Distribution can have the following values:
If the argument is a list, then the first element in the list is taken. If this is also a list, then the process is repeated. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Parameter1 |
Specifies the first parameter for the distribution to be calculated. Permitted data structures are Scalar value. All numeric data types are permitted. If the argument is a list, then the first element in the list is taken. If this is also a list, then the process is repeated. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Parameter2 |
If necessary, specifies the second parameter of the distribution to be calculated. Permitted data structures are Scalar value. All numeric data types are permitted. If the argument is a list, then the first element in the list is taken. If this is also a list, then the process is repeated. |
Remarks
The result always has the data type 64-bit floating point.
The continuous probability density f(x) and distribution function F(x) of the normal distribution with expected value μ and variance σ² are given by:
The continuous probability density f(x) and distribution function F(x) of the logarithmic normal distribution with the parameters μ and σ² are given by:
The continuous probability density f(x) and distribution function F(x) of the exponential distribution with the parameter α (inverse scale parameter) are given by:
The continuous probability density f(x) and distribution function F(x) of the Weibull distribution with the parameters α and β (shape parameter) are given by:
Note: in the literature, the characteristic lifetime T is often used as an alternative to the parameter α (and β is denoted by k). The following relation applies here:
Similarly, the inverse scale parameter λ = 1/T is often used in the literature instead of the parameter α. The following therefore applies:
The continuous probability density f(x) and distribution function F(x) of the chi-square distribution with the parameter n (number of degrees of freedom) are given by:
P(n1,n2) denotes the regularized, incomplete gamma function.
The continuous probability density f(x) and distribution function F(x) of the Student t-distribution with the parameter n (number of degrees of freedom) are given by:
I(z,n1,n2) denotes here (and in the following) the regularized, incomplete beta function.
The continuous probability density f(x) and distribution function F(x) of the F-distribution (Fisher distribution) with the parameters m (number of degrees of freedom in the denominator) and n (number of degrees of freedom in the numerator) are given by:
The discrete probability density f(k) and distribution function F(x) of the binomial distribution with the parameters n (number of trials) and p (probability of success or hit) are given by:
The discrete probability density f(k) and distribution function F(x) of the Poisson distribution with the parameter λ (mean event rate) are given by:
Available in
Option Statistics
Examples
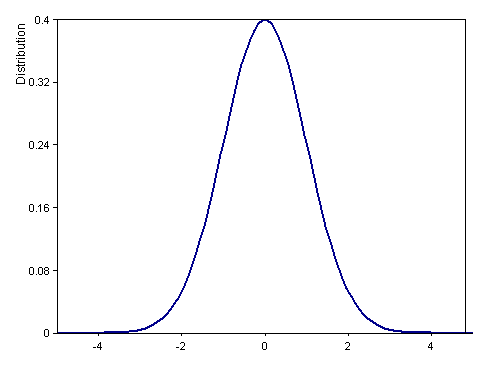
Dim x = Series(-5, 5, 0.05)
Signal(Distribution(x, DISTRIBUTION_NORMAL + DISTRIBUTION_DENSITY, 0, 1), x)
Calculates the density function of the standard normal distribution (mean 0, variance 1) in interval [-5, 5].
See Also
EmpiricalDistribution Function
References
[1] "Hartung, Joachim": "Statistik, 9. Auflage". "Oldenbourg Verlag GmbH, München", 1993. ISBN 3-486-22055-1.