ArcTan2 (FPScript)
Calculates the arctangent with two arguments.
Syntax
ArcTan2(Y, X)
The syntax of the ArcTan2 function consists of the following parts:
Part |
Description |
|---|---|
Y |
The first argument of the function. Corresponds to the Y coordinate of a point in a two-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system. All data structures are allowed. All real data types are permitted. |
X |
The second argument of the function. Corresponds to the X coordinate of a point in a two-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system. All data structures are allowed. All real data types are permitted. |
Remarks
The result has the unit rad.
The function finds the angle φ when converting from Cartesian coordinates (x, y) to polar coordinates (r, φ).
The function ArcTan2(y, x) can be defined as follows: If x and y are real numbers with r = sqrt(x^2 + y^2), then the following applies:
x = r * cos(ArcTan2(y, x)),
y = r * sin(ArcTan2(y, x)).
This means that: (r, ArcTan2(y, x)) is the polar coordinate graph of the point with the Cartesian coordinates (x, y).
The function ArcTan2 is defined as follows:
The value range of ArcTan2(y, x) is the half-open interval ]-PI, PI].
If at least one argument is a data series or data matrix, the calculation is performed on a per-element basis and the result is also a data series or a data matrix. The number of rows and possibly number of columns of both arguments must match, except if an argument is a scalar value. A scalar argument is expanded in this case to include the number of values of the non-scalable argument.
If the function is applied to signals, signal series or space curves, the result is in turn a signal or signal series or space curve. The result’s Y component is the result of applying the function to the Y components of the two arguments. The X and possibly Z component of the result corresponds favorably to the X and possibly Z component from the first argument; otherwise it is the X and possibly Z component from the second argument.
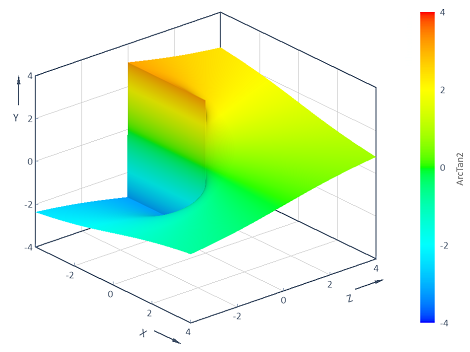
Visualization of the ArcTan2 function with 2 variables
Calculates the ArcTan2 function y = ArcTan2(z, x) across the two-dimensional (x, z) range [-4, 4] x [-4, 4]. The visualization in a 3D contour diagram results in the following:
If the argument is a list, then the function is executed for each element of the list and the result is also a list.
Available in
FlexPro Basic, Professional, Developer Suite
Examples
ArcTan2(7, -5) |
Results in 2.191. |
Dim z = -5 + 7i |
The call byPhase is equivalent to ArcTan2(Imag(z), Real(z)), i.e. in this case to ArcTan2(7, -5) |
ArcTan2(DataSeries1, DataSeries2) |
Calculates the ArcTan2() of two equally long data series. The calculation takes place on a per element basis and the result is also a data series. |
ArcTan2(Sig1, Sig2) |
Calculates the ArcTan2() of two equally long signals. The calculation takes place on a per element basis and the result is equivalent to Signal(ArcTan2(Sig1.Y, Sig2.Y), Sig1.X). |
